Human’s
excretion system
a. Process
of spending the rest of the substances in the human body can be divided into
three kinds, namely:
1. Defecation: the process of spending the
leftovers called feces and excreted through the anus.
2. Excretion: expenditures materials useless
derived from metabolic waste or excess material of a cell or an organism
(Sumanto, 1996: 102).
3. Secretion: the expenditure by the cell sap
and glands. Issued sap is still useful for processes in the body physiology.
The sap usually contains enzymes.
b. Human’s
excretion organs
Disposal of substances that are not useful in
the body called the organs of excretion. Excretion organs include:
Lungs
c. Excretion system function
Dispose of waste products of metabolism
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) - Lungs
- T Toxins, Waste nitrogen - Kidney
- Medicine - Kidney
- Sweat - Leather
- Bile - Heart
d. Renal -
urinary system function
Throw away metabolic waste:
- Waste nitrogen
- Medications
- Toxins
Set:
- The water balance in the body
- The content of electrolyte
- Acid-Base fluid blood
- Blood Pressure
- Production of red blood cells
- Activation of vitamin D
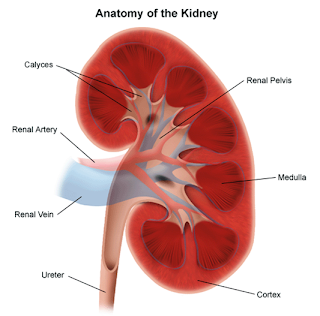
e. anatomy
of kidney
Urine is formed through 3 stages:
1. Filtration
2. reabsorption
3. Secretion / Augmentation
urinary system
urinary system
g. kidney’s
disorders:
1. Kidney
stones: the stones of calcium deposits in the renal pelvis and salt.
Cause: often
hold urine and less drinking.
2. Diabetes
Mellitus: In urine containing glucose. This is because of the sugar levels in
the blood are high.
3. Diabetes
insipidus: Frequent bowel movements are great (up to 20-30 times). It Occurs
due to lack of ADH hormone.
kidney stones: :kaget:
kidney stones: :kaget:











No comments:
Post a Comment